Data Structure and Algorithm Notes 数据结构与算法笔记
CN-blogs
Updating
本章语言以
Python为主, 面试时需要背下文中的函数而不能靠 vibe coding.
本章 abbr: ITV: Interview 回答方法
1 Time/Space Complexity 时间/空间复杂度
时间看循环, 空间看数组
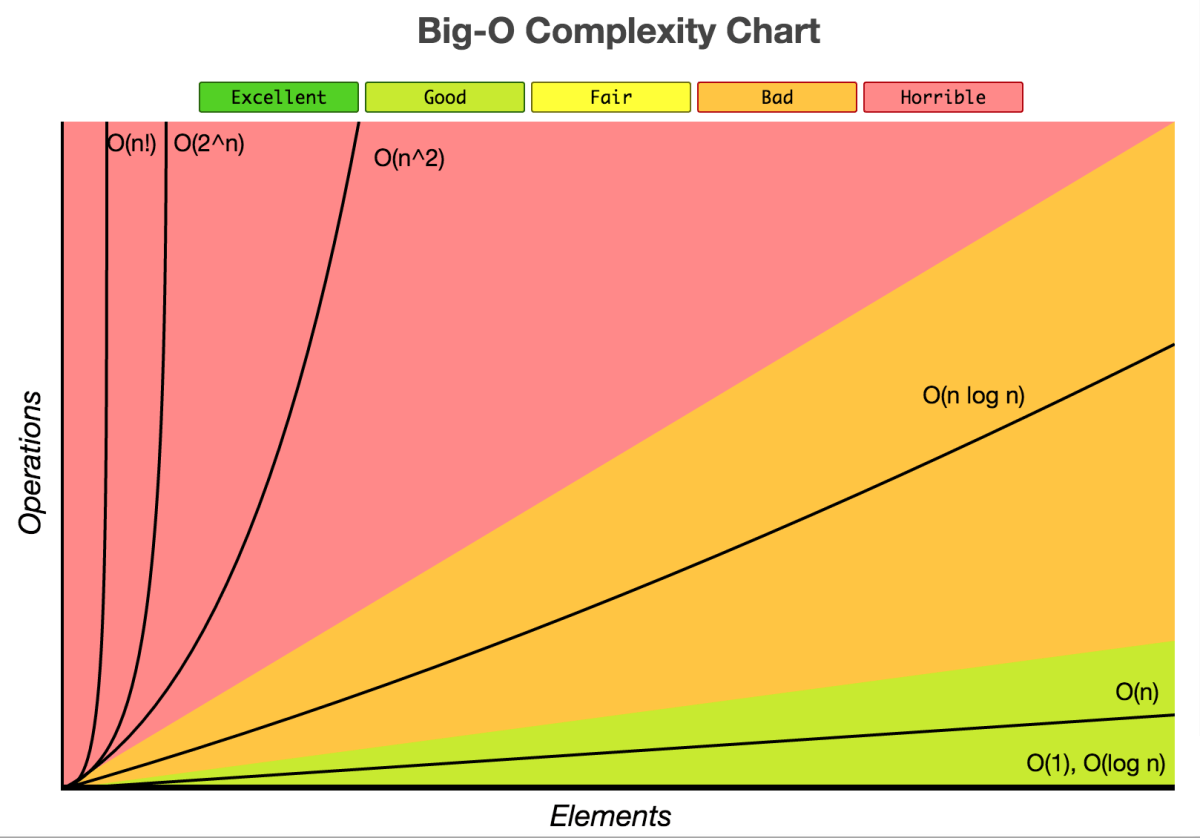
Time Complexity 不 care 系数, 只 care 随着问题 elements 规模的增长 operations 数量的增长情况 
\(\mathcal{O}(n \log n)\) 这种想象成循环嵌套, \(\mathcal{O}(n+m)\) 这种想象成循环并列 大部分算法停机时间不确定, 用最坏情况来思考复杂度!
空间复杂度一般都是 \(\mathcal{O}(1)\) 或 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\), \(\mathcal{O}(n^2)\) 比较少, \(\mathcal{O}(n)\) 和 \(\mathcal{O}(n\log n)\) 非常少.
- 递归一般会有个 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\), 因为要用到递归栈.
时间和空间是 trade-off 关系, 二者只能求其一. 一般来说, 由于空间 cheap, 时间贵, 所以更看重时间复杂度.
2 Data Structure 数据结构
2.1 General 共性
- 所有数据结构都要考虑1以下做操作 (abbr. ASID) 是否方便 (时间复杂度):
- Access 访问: index 找 element (数组)
- Search 搜索: element 找 index (数组)
- Insertion 插入
- Deletion 删除
1 ITV 请对比两个数据结构.
2.2 Array 数组
- Array 数组: 连续内存空间! 相同类型数据!
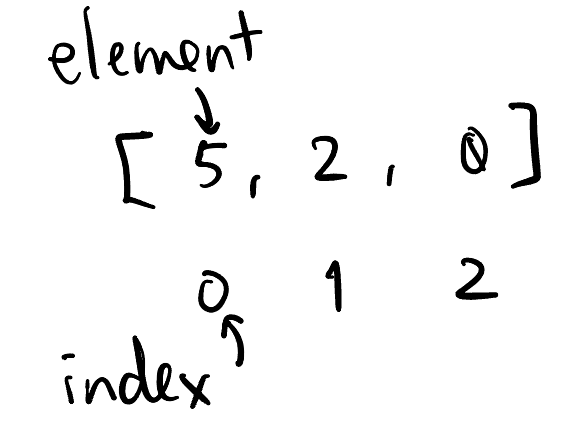
区分: Element 元素 vs Index 索引 (Figure 1)
ASID: \(\mathcal{O}(1)\), \(\mathcal{O}(n)\), \(\mathcal{O}(n)\), \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- 适合读多写少的场景.
- 但是
append操作是 \(\mathcal{O}(1)\) 的.